British households are boosting the profits of Chinese and Qatari Government-backed funds, which are among the groups benefiting from a 38% increase in the costs of running the country’s gas network.
A new report from the Warm This Winter campaign and Future Energy Associates has examined the ownership and revenue streams of firms running the nation’s gas infrastructure. [1]
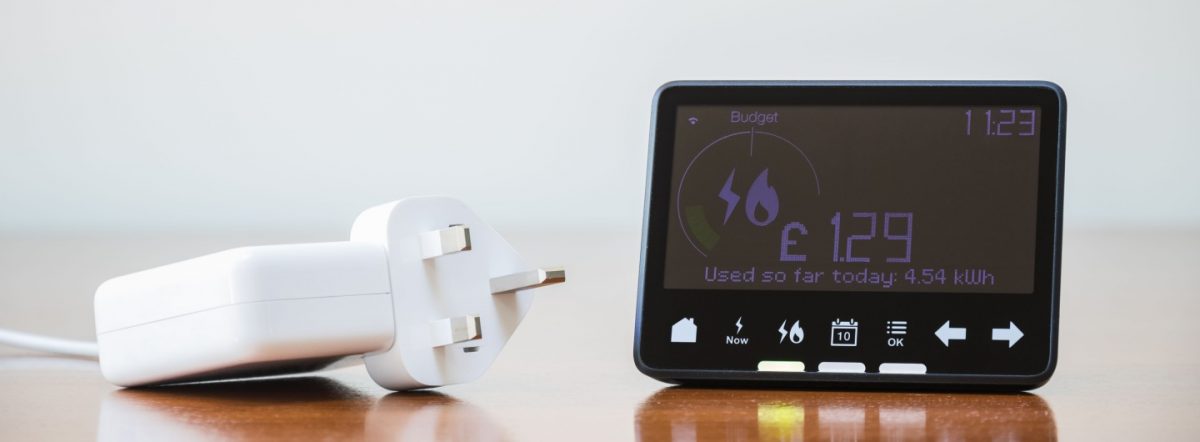
The cost of running the gas network is charged to customers through gas unit costs and standing charges. The estimated price each household contributes has risen from £118.53 a year in 2021 to £163.69 a year from 1 April 2024 (a 38% increase). [2]
Unit costs are also driven by wholesale gas costs. Gas unit costs paid by households more than tripled at the height of the energy bills crisis and even after the latest Ofgem price cap change, every unit of gas remains 73% above 2021 levels. The daily gas standing charges customers face have also continued to increase and will not peak until the coming months, reaching 15% above 2021 levels from 1 April 2024. [3]
Of the significant owners of gas infrastructure operators, just one company is headquartered in the UK [4]. Among the 12 other owners are the sovereign wealth funds of Qatar and China, investment firms from Australia, Canada, Germany, Hong Kong and the USA alongside additional Australian and Canadian pension funds.
Among the firms profiting from the misery of increased energy bills is Macquarie, the Australian finance giant at the centre of recent Southern Water and Thames Water scandals. [5]
Macquaire co-owns 80% of National Gas, the national gas network as well as part-owning the UK’s largest regional gas distribution network company, Cadent, which supplies gas to 11 million homes.
The report sets out that Gas Distribution Networks (GDNs) operate as natural monopolies and that the complexity in negotiations between the regulator and the firms risks tilting the balance in favour of the industry, potentially leading to excess profits at the expense of consumers.
Among the criticisms of the negotiation process are the reliance on long-term cost forecasting, informational advantage firms hold over their costs and their ability to hire expensive lobbyists and consultants which poses a risk of regulatory decisions favouring the industry, resulting in unjustifiably high prices for consumers and excess profits for the companies.
Starting from 2026, energy consumers could also face an annual bill increase of up to £43 to fund the decommissioning of the gas network, as highlighted in a new Ofgem consultation on price controls for gas and electricity transmission networks.
Fiona Waters, spokesperson for the Warm This Winter campaign, which commissioned the report said:
“Once again the British public is being gaslighted by an opaque and broken energy system which sees huge amounts of obscene profits going overseas and inflates bills for ordinary people who are still paying 60% more than they did three years ago.
“Families, pensioners, children and the poor are freezing as energy companies generate billions of pounds in profit each and every week.”
A spokesperson for the End Fuel Poverty Coalition, commented:
“This murky web of international investors with deep pockets and influence are heaping pain on the nation’s households.
“The regulator is operating with one hand tied behind its back and it needs to be given powers to ensure that the firms that operate our gas network do so in the best interests of the public, not their shadowy owners.
“Ultimately, this is an industry that is dying on its feet as we move toward cleaner, safer heating systems for our homes. But we should not let these vampire funds suck cash out of hard working families’ pockets as they decommission the network.”
Dylan Johnson from Future Energy Associates commented:
“Government regulation is crucial to control the prices charged by these companies, ensuring efficiency and security of supply without unfairly burdening consumers.
“This regulatory process involves negotiations between the companies, who aim to maximise their profits, and regulators, tasked with balancing affordable consumer prices with the need for efficient and reliable service.
“At the moment the balance is not right and the regulator needs to take a stronger stance in negotiations.”
Jonathan Bean, from Fuel Poverty Action said:
“It’s frightening that the Government has let a notorious investor take control of a large chunk of our energy infrastructure. It means higher energy bills for us all.”
The report makes several recommendations for Ofgem to consider, including proposals to deliver immediate consumer rebates by network companies to address profits not in consumers’ interests and the use of real market data instead of long-term forecasts.
The report also finds that consumer bodies should be empowered to request price control reviews in cases of excessive financial returns and ensuring balanced representation of consumer interests in regulatory decisions.
ENDS
This news story relates to England, Scotland and Wales only.
[1] Warm This Winter Tariff Watch: Gas Networks Report (March 2024): Download the full report.
[2] The Bank of England inflation calculator suggests that a solely inflationary linked increase in these costs would be from £118 to £139 – 18% increase.
[3] End Fuel Poverty Coalition records: https://www.endfuelpoverty.org.uk/about-fuel-poverty/ofgem-price-cap/
[4] Gas network owners:
The gas transmission network (described as the “motorway of the gas network”) is run by National Gas, which is owned by a consortium 80% of Macquarie Asset Management, British Columbia Investment Management Corporation, and National Grid plc (20%).
Macquarie Group, an Australian powerhouse in the financial services sector which also controls parts of the UK water and sewage network, has emerged as a dominant force in the global infrastructure sphere, most notably through its ownership of National Gas in the UK. The British Columbia Investment Management Corporation (BCI) is a pivotal but relatively obscure financial institution managing the pensions of about 525,000 British Columbians. National Grid is one of the world’s largest utilities firms and is listed on the London stock exchange.
The gas distribution network (described as the “local roads of the gas network”) is ultimately owned by eleven firms:
| Entity |
Type of firm (HQ) |
GDN Ownership Relevance |
| Qatar Investment Authority |
Sovereign wealth fund (Qatar) |
Owns stakes in critical infrastructure, including gas sectors. |
| Macquarie Asset Management |
Investment Manager (Australia) |
Macquarie invests and manages large numbers of global assets with a strong focus on infrastructure. |
| Hermes Investment Management |
Private company – investment management (USA*) |
Investment Management firm that invests in a broad range of low risk assets. |
| China Investment Corporation |
Sovereign wealth fund (China) |
Involved in owning critical infrastructure, focusing on energy sectors. |
| Allianz Capital Partners |
Private company – asset management (Germany) |
Specialises in infrastructure and renewable energy investments. |
| Brookfield Infrastructure Partners |
Public company – infrastructure management (Canada) |
Owns diversified infrastructure assets, including utilities. |
| Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan Board |
Pension fund (Canada) |
Invests in a variety of sectors, including infrastructure, with a focus on stable, long-term returns. |
| Global Infrastructure Partners |
Private company – investment (USA) |
Manages a broad range of infrastructure assets; recent acquisition by BlackRock raises profile. |
| CK Hutchison Holdings & Affiliates |
Public company – conglomerate (Hong Kong / Cayman Islands) |
Owns a significant stake in utilities through multinational conglomerate structure. |
| Power Assets Holdings |
See above (Hong Kong) |
Part of the CK group, focuses on electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. |
| State Super |
Pension fund (Australia) |
Invests in critical infrastructure, including significant stakes in the aviation sector. |
| * Hermes Investment Management (registered in the UK) is owned by Federated Hermes, a US-based investment manager. |
[5] Described by critics as a “vampire kangaroo”, in 2022, Southern faced allegations of “environmental vandalism” for releasing untreated sewage continuously for over 3,700 hours at 83 bathing water beaches in just the first eight days of November. The repercussions of a substantial debt load and potentially insufficient investment during the Australian company’s ownership of Thames Water continue to linger, with ongoing incidents of sewage leaks contaminating waterways, impacting farms and residences, and causing harm to wildlife years after the company divested its remaining stake in Thames Water.