End Fuel Poverty Coalition members have reacted with growing anger to the Chancellor’s Spring Statement.
A spokesperson for the Coalition commented:
As one MP in the chamber shouted, “is that it?”
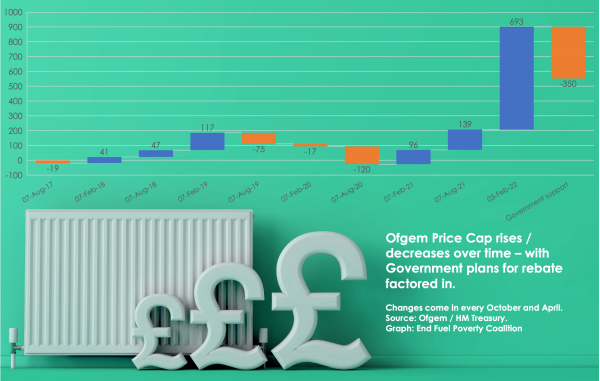
The unexpected VAT cut on installing renewable or energy efficiency measures, the increase to Household Support Funds and the promised tax cuts, will no doubt help some people.However, the fuel poverty crisis gripping this country will affect over 6.3m households from 1 April.
And for these people – including the 2.5m families with children in fuel poverty – there was very little in the Spring Statement.
End Fuel Poverty Coalition members have called for urgent help for households in fuel poverty now combined with a long-term plan to improve energy efficiency of our homes and investment in a sustainable, renewable-led, energy mix.
None of these things were delivered.
Sadly, the Chancellor has once again ignored those in fuel poverty – including the 14,000 homes in his own constituency. He must come back to Parliament at the earliest opportunity and set out how the Government will help those who will continue to suffer.
Commenting on today’s Spring Statement, Dan Paskins, Director of UK Impact at Save the Children, said:
The chancellor is burying his head in the sand. In today’s statement he’s refused to face up to the reality of rising prices or to step in and shield the children hardest hit.
For families on low incomes this crisis has become unbearable. Parents we work with tell us that there’s nothing left to cut back. They’re being forced to skip meals, turn off the heating, and take on unsustainable amounts of debt. Children are going to school hungry because food budgets are stretched so thin.
The measures the chancellor has announced will benefit those on middle and higher incomes most and won’t come to close to closing the gap rising prices have left in family budgets.
A 5p cut to fuel duty coupled with an increase to the national insurance threshold translates into an additional £18.40 per month for the poorest families, in the context of a real-terms income cut of £55 a month.
And while we welcome the continuation of the Household Support Fund, it’s designed for one-off unexpected costs, so this measure is grossly insufficient when families are facing soaring costs every day.
The government must do more. The best way to support the families who are struggling most is to increase social security payments to match the rate at which prices are increasing.
Dr Doug Parr, policy director at Greenpeace UK, said:
Right now millions of people are paying through the nose to heat homes which are so poorly insulated the warmth shoots right outside.
Cutting VAT on insulation, solar panels and heat pumps is a welcome start to ending that huge waste of energy, helping keep bills down and cut our gas use.
But if the chancellor’s serious about tackling the issue then it can only be the start. We need to see around £10bn of support, part raised by a windfall tax on oil and gas companies, for delivering the help families need to install the clean technologies that will get us off gas.
That should include finally fulfilling the full Conservatives manifesto pledge of £9.2bn towards energy efficiency, with more support grants available and greater backing to help the industry train up and deploy the tens of thousands of jobs this area offers.
National Energy Action experts tweeted:
Zero VAT on energy efficiency will make public money go further on schemes
More money for LAs to support households is good, but provision is inconsistent. Would have been better to increase existing energy schemes
Fuel duty cut will help many, but will help richer people most https://t.co/0TjUW5fSJC
— Matt Copeland (@Matt_Copeland1) March 23, 2022
Meanwhile, the Joseph Rowntree Foundation set out why the National Insurance Changes will not benefit those in fuel poverty:
Rise in NICs thresholds is very expensive for a small gain for low income working families and nothing for those with no-one in work.
The Chancellor has chosen to prioritise a tax break for middle and high income households over preventing a real terms cut to benefits— Dave Innes (@dminnes) March 23, 2022
And the New Economics Foundation explained how the petrol price cut will not help low income households:
A 5p cut to fuel duty is worth less than £2/month for the poorest 10% of households #SpringStatement
— Alfie Stirling (@alfie_stirling) March 23, 2022
More reaction will follow.
Image: Shutterstock